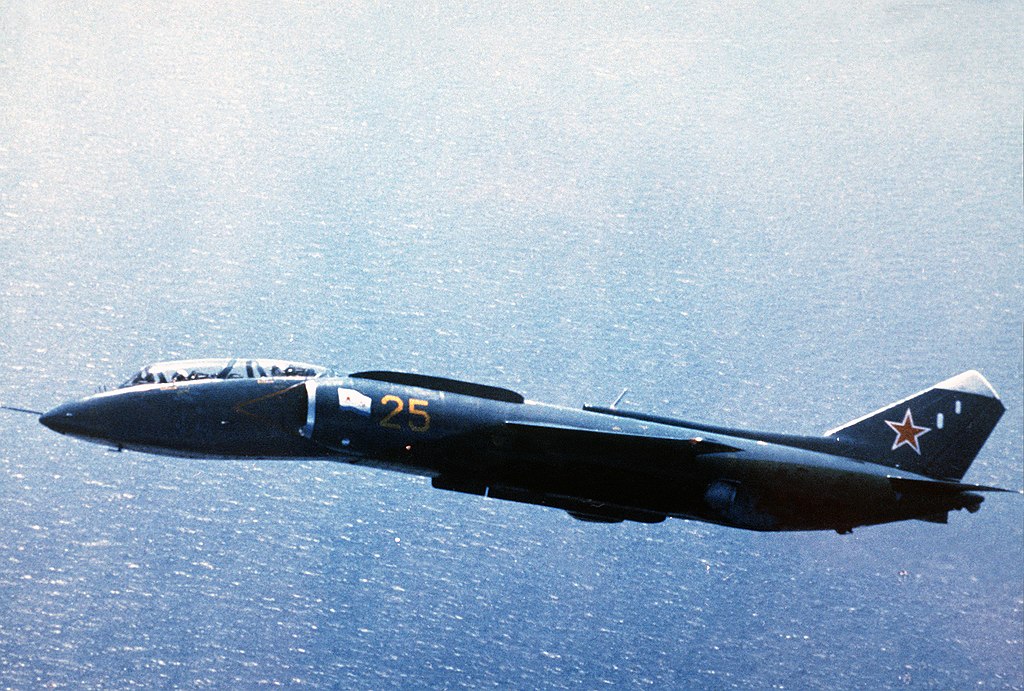
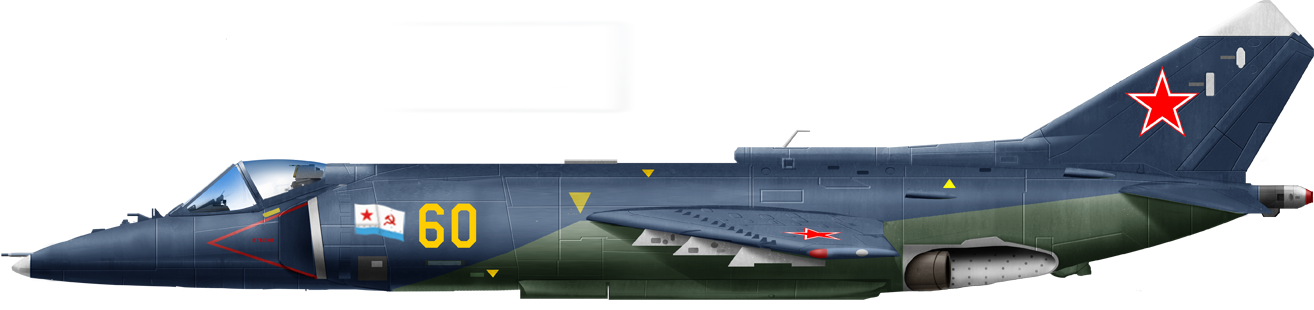
The Yak 38 in brief

The Yakovlev Yak-38 was the Soviet Union's first operational vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft and the only VTOL strike fighter to enter service with the Soviet Navy. Introduced in the early 1970s, it was developed by the Yakovlev Design Bureau as part of the Soviet Navy's initiative to equip its small aircraft carriers, such as the Kiev-class, with fighter aircraft.
Thus VTOL strike fighter had its first Flight in 1971 and it entered service in 1976 but was retired in 1991 following the dissolution of the Soviet Union. It was never used in combat and never exported. The Yak-38 had a unique VTOL configuration, relying on three engines: A single Tumansky R-27V-300 turbojet for forward propulsion. Two smaller RD-36-35FVR lift engines mounted behind the cockpit to provide vertical thrust. Maximum speed of approximately 1,050 km/h (650 mph).

Range: Limited operational range of about 1,300 km (800 miles), reduced further in VTOL operations due to high fuel consumption.
Typically carried unguided rockets, bombs, or air-to-air missiles like the R-60 (NATO: AA-8 Aphid) and Optionally equipped with a 23mm cannon pod. It was deployed primarily aboard the Kiev-class aircraft carriers, the Yak-38 was intended to support naval operations in contested areas. It was often criticized for its limited payload, range, and performance compared to Western VTOL jets like the British Harrier. While it was technologically significant as a Soviet VTOL jet, the Yak-38's limitations made it less effective in combat roles. It served as a stepping stone for Soviet VTOL technology and led to the development of more advanced concepts, like the Yak-141 (a prototype supersonic VTOL fighter).
Variants

Yak-36M "Forger"
Initial pre-production version, differing slightly from the Yak-38. It weighed 6,650 kg (14,660 lb) compared to the Yak-38's 7,370 kg (16,250 lb) and the engines were slightly less powerful.Yak-38 "Forger-A"
The Yak-38 was the first production model, it first flew on 15 January 1971, and entered service with the Soviet Naval Aviation on 11 August 1976. A total of 143 Yak-38s were produced.Yak-38M "Forger-A"
The Yak-38M was an upgraded version of the Yak-38, the main difference being the new Tumansky R-28V-300 and Rybinsk RD-38 engines. The maximum takeoff weight in VTOL was increased from 10,300 kg (22,700 lb) to 11,300 kg (24,900 lb) and was 12,000 kg (26,000 lb) in short takeoff mode. The air intakes were slightly widened and the underwing pylons reinforced to carry a 2,000 lb (910 kg) weapons load. The Yak-38M entered service with the Soviet Naval Aviation after June 1985; 50 Yak-38M were produced.Yak-38U "Forger-B"
Two-seat training version of the Soviet Naval Aviation. This version differed from the basic aircraft in having an enlarged fuselage to accommodate a two-seat cockpit. The Yak-38U entered service on 15 November 1978. Thirty-eight Yak-38U were produced, the final aircraft was delivered in 1981.
⚙ Yak-38 specifications | |
| Empty Weight | 7,385 kg (16,281 lb) |
| Max Takeoff weight | 11,300 kg (24,912 lb) |
| Lenght | 16.37 m (53 ft 8 in) |
| Wingspan | 7.32 m (24 ft) |
| Height | 4.25 m (13 ft 11 in) |
| Wing Area | 18.5 m2 (199 sq ft) |
| Engines | 1× Tumansky R-28 V-300 66.7 kN, 2 × Rybinsk RD-38 turbojets 31.9 kN |
| Top Speed, sea level | 1,050 km/h (650 mph, 570 kn) |
| Range | 1,300 km (810 mi, 700 nmi) |
| Ceiling | 11,000 m (36,000 ft) |
| Armament | GSh-23L 23 mm gun pod, hard pts for 2,000 kg (4,400 lb) |
| Crew | 1 pilot |
Read More/Src

(To come)
Books
Links
Videos
Model Kits
3D
- Lohner E (1913)
- Macchi M3 (1916)
- Macchi M5 (1918)
- Ansaldo ISVA (1918)
- Short S.38 (1912)
- Sopwith Baby (1916)
- Short 184 (1916)
- Fairey Campania (1917)
- Sopwith Cuckoo (1917)
- Felixstowe F.2 (1917)
- Friedrichshafen FF 33 (1916)
- Albatros W4 (1916)
- Albatros W8 (1918)
- Hanriot HD.2
- Grigorovich M5 (1915)
- Grigorovich M9 (1916)
- IJN Farman MF.7
- IJN Yokosho Type Mo
- Yokosho Rogou Kougata (1917)
- Yokosuka Igo-Ko (1920)
- Curtiss N9 (1916)
- Aeromarine 39
- Vought VE-7
- Douglas DT (1921)
- Boeing FB.5 (1923)
- Boeing F4B (1928)
- Vought O2U/O3U Corsair (1928)
- Blackburn Blackburn (1922)
- Supermarine Seagull (1922)
- Blackburn Ripon (1926)
- Fairey IIIF (1927)
- Fairey Seal (1930)
- LGL-32 C.1 (1927)
- Fokker T.II (1921)
- Caspar U1 (1921)
- Dornier Do J Wal (1922)
- Rohrbach R-III (1924)
- Mitsubishi 1MF (1923)
- Mitsubishi B1M (1923)
- Yokosuka E1Y (1923)
- Nakajima A1N (1927)
- Nakajima E2N (1927)
- Mitsubishi B2M (1927)
- Nakajima A4N (1929)
- CANT 18
WW1
✠ K.u.K. Seefliegerkorps:
 Italian Naval Aviation
Italian Naval Aviation
 RNAS
RNAS
 Marineflieger
Marineflieger
 French Naval Aviation
French Naval Aviation
 Russian Naval Aviation
Russian Naval Aviation
 IJN Air Service
IJN Air Service
 USA
USA
Interwar
 Interwar US
Interwar US
 Interwar Britain
Interwar Britain
 Interwar France
Interwar France
 Interwar Netherlands
Interwar Netherlands
 Interwar Germany
Interwar Germany
 Interwar Japan
Interwar Japan
 Interwar Italy
Interwar Italy
- Curtiss SOC seagull (1934)
- Grumman FF (1931)
- Curtiss F11C Goshawk (1932)
- Grumman F2F (1933)
- Grumman F3F (1935)
- Northrop BT-1 (1935)
- Grumman J2F Duck (1936)
- Consolidated PBY Catalina (1935)
- Brewster/NAF SBN-1 (1936)
- Curtiss SBC Helldiver (1936)
- Vought SB2U Vindicator (1936)
- Brewster F2A Buffalo (1937)
- Douglas TBD Devastator (1937)
- Vought Kingfisher (1938)
- Curtiss SO3C Seamew (1939)
- Douglas SBD Dauntless (1939)
- Grumman F4F Wildcat (1940)
- F4U Corsair (NE) (1940)
- Brewster SB2A Buccaneer (1941)
- Grumman TBF/TBM Avenger (1941)
- Consolidated TBY Sea Wolf (1941)
- Grumman F6F Hellcat (1942)
- Curtiss SB2C Helldiver (1942)
- Curtiss SC Seahawk (1944)
- Grumman F8F Bearcat (1944)
- Ryan FR-1 Fireball (1944)
- Douglas AD-1 Skyraider (1945)
Fleet Air Arm
- Fairey Swordfish (1934)
- Blackburn Shark (1934)
- Supermarine Walrus (1936)
- Fairey Seafox (1936)
- Blackburn Skua (1937)
- Short Sunderland (1937)
- Blackburn Roc (1938)
- Fairey Albacore (1940)
- Fairey Fulmar (1940)
- Grumman Martlet (1941)
- Hawker sea Hurricane (1941)
- Brewster Bermuda (1942)
- Fairey Barracuda (1943)
- Fairey Firefly (1943)
- Grumman Tarpon (1943)
- Grumman Gannet (1943)
- Supermarine seafire (1943)
- Blackburn Firebrand (1944)
- Hawker Sea Fury (1944)
IJN aviation
- Yokosuka E6Y (1930)
- Aichi D1A "Susie" (1934)
- Mitsubishi A5M "Claude" (1935)
- Nakajima A4N (1935)
- Yokosuka B4Y "Jean" (1935)
- Mitsubishi G3M "Nell" (1935)
- Nakajima E8N "Dave" (1935)
- Kawanishi E7K "Alf" (1935)
- Nakajima B5N "Kate" (1937)
- Kawanishi H6K "Mavis" (1938)
- Aichi D3A "Val" (1940)
- Mitsubishi A6M "zeke" (1940)
- Nakajima E14Y "Glen" (1941)
- Nakajima B6N "Jill" (1941)
- Mitsubishi F1M "pete" (1941)
- Aichi E13A Reisu "Jake" (1941)
- Kawanishi E15K Shiun "Norm" (1941)
- Nakajima C6N Saiun "Myrt" (1942)
- Yokosuka D4Y "Judy" (1942)
- Kyushu Q1W Tokai "Lorna" (1944)
Luftwaffe
- Arado 196 (1937)
- Me109 T (1938)
- Blohm & Voss 138 Seedrache (1940)
Italian Aviation
- Savoia-Marchetti S.55
- IMAM Ro.43/44
- CANT Z.501 Gabbiano
- CANT Z.506 Airone
- CANT Z.508
- CANT Z.511
- CANT Z.515
French Aeronavale
- GL.300 (1926-39)
- Levasseur PL.5 (1927)
- Potez 452 (1935)
- Loire 210 (1936)
- Loire 130 (1937)
- LN 401 (1938)
Soviet Naval Aviation
- Shavrov SH-2 (1928)
- Tupolev TB-1P (1931)
- Beriev MBR-2 (1930)
- Tupolev MR-6 (1933)
- Tupolev MTB-1 (1934)
- Beriev Be-2 (1936)
- Polikarpov I16 naval (1936)
- Tupolev MTB-2 (1937)
- Ilyushine DB-3T/TP (1937)
- Beriev Be-4 (1940)
-
Skoda Š-328V
R-XIII Idro
Fokker C.XI W (1934)
Rogožarski PVT-H (1938)
WW2
- De Havilland Sea Vixen
- Hawker Sea Hawk
- Supermarine Scimitar
- Blackburn Buccaneer
- Hawker Sea Harrier
- Douglas A4 Skyhawk
- Grumman F9F Panther
- Vought F8 Crusader
- McDonnell-Douglas F-4 Phantom-II
- North Am. A5 Vigilante
- TU-142
- Yak 38 forger
☢ Cold War
✧ NATO
 Fleet Air Arm
Fleet Air Arm
 US Navy
US Navy
☭ Warsaw Pact
Merch
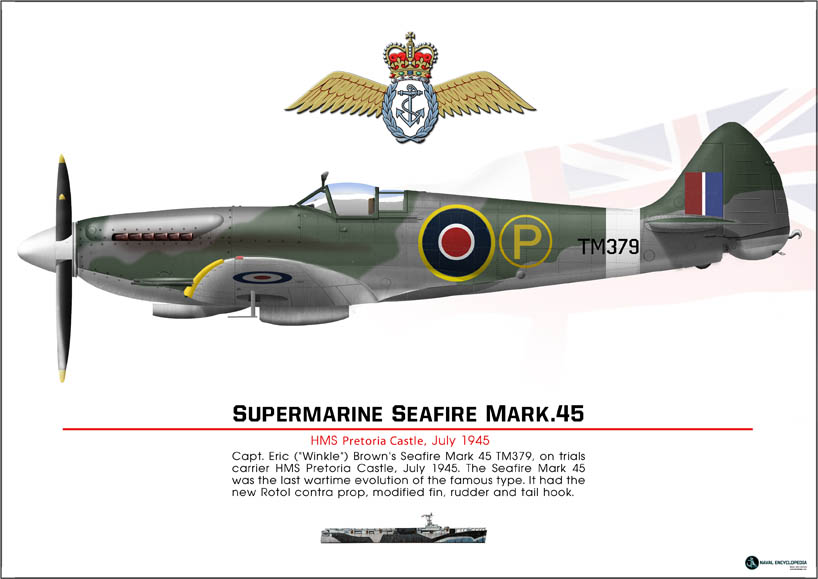
Seafire Mark 45; HMS Pretoria Castle

Zeros vs its aversaries

Aichi D3A “Val” Junyo

Mitsubishi A5M poster

F4F wildcat

Macchi M5
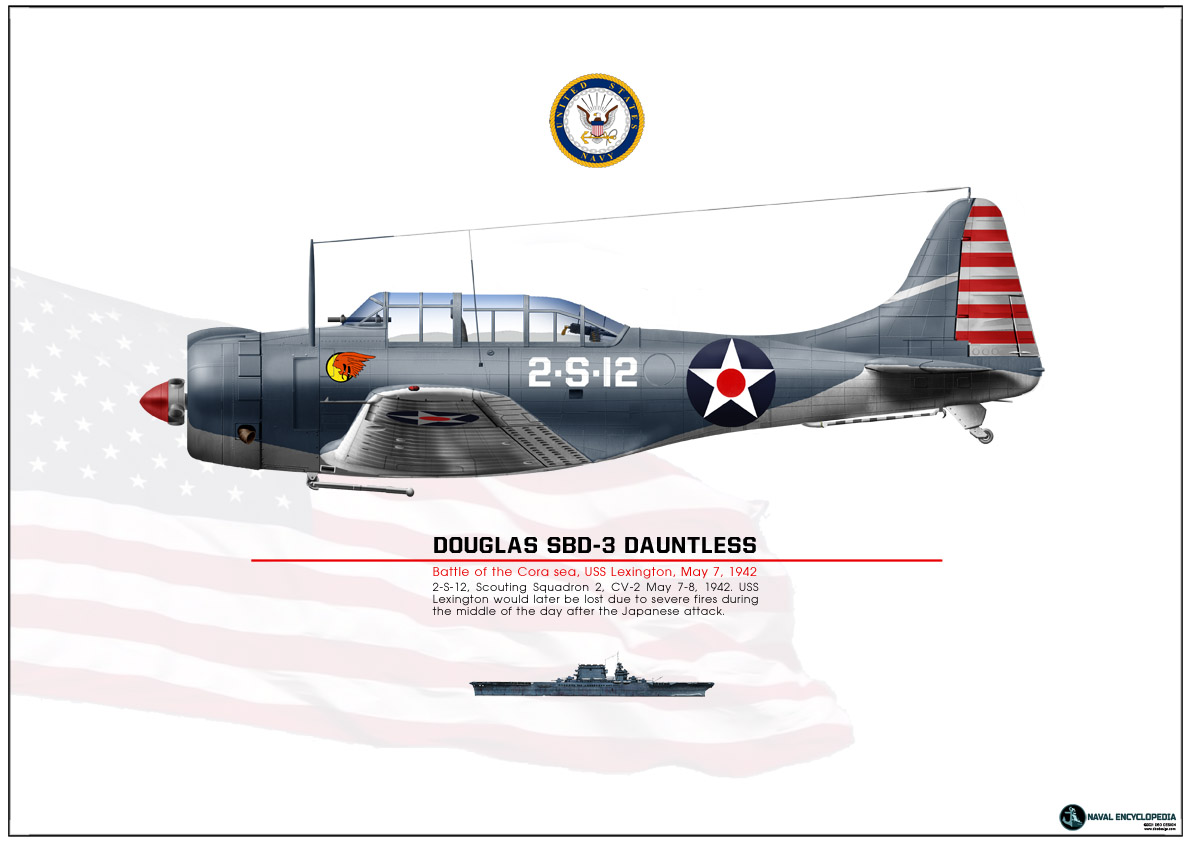
SBD Dauntless Coral Sea
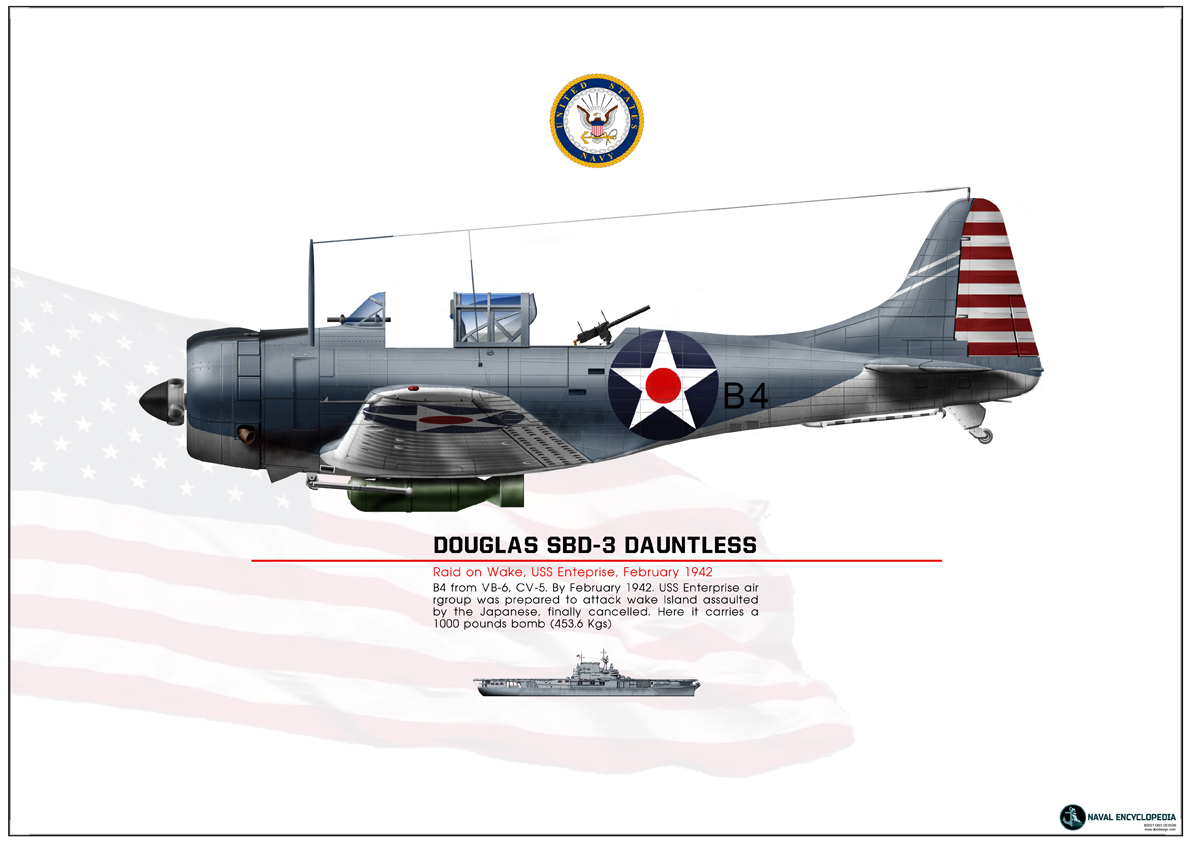
SBD Dauntless USS Enterprise

SBD-4 CV22