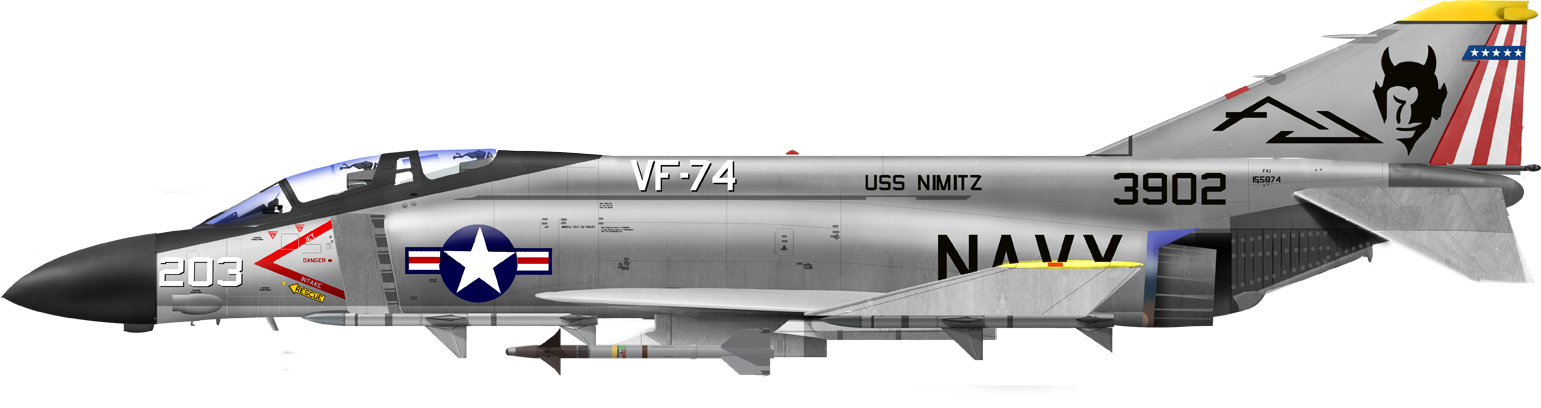
The Phantom II in Brief

The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II is a legendary American tandem two-seat, twin-engine, all-weather, long-range supersonic jet interceptor and fighter-bomber originally developed by McDonnell Aircraft for the United States Navy. It first flew on May 27, 1958, and entered service in 1960. The Phantom was a highly versatile aircraft used by the U.S. Navy, Marine Corps, and Air Force, and it was also adopted by several other nations.
The F-4 is powered by two General Electric J79-GE-17 afterburning turbojet engines, each providing 17,900 lbf (79.4 kN) of thrust with afterburner. Speed and Range: It has a maximum speed of Mach 2.23 (1,472 mph, 2,370 km/h) and a combat range of approximately 367 miles (592 km). It was armed with Air-to-air missiles: AIM-7 Sparrow, AIM-9 Sidewinder, carried Various bombs and rockets, including precision-guided munitions while having Internal M61 Vulcan 20mm rotary cannon (F-4E variant).
The F-4 featured advanced avionics for its time, including radar, electronic countermeasures, and targeting systems. Its Service ceiling was 60,000 feet (18,300 meters) and the Rate of climb was 41,300 feet per minute (210 m/s)

In the Vietnam War, The F-4 Phantom II played a significant role, serving as the primary air superiority fighter for the U.S. military. It was also used extensively in ground-attack and reconnaissance missions. It also fought in the Yom Kippur War (1973), Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988) and served across the globe as fighter-bomber, interceptor, reconnaissance, Wild Weasel (SEAD - Suppression of Enemy Air Defenses). It is considered one of the most versatile and durable aircraft of the Cold War era with over 5,000 built, making it one of the most produced American supersonic military aircraft. It was used by several countries including the United Kingdom, Japan, Germany, and Israel. The Phantom remained in service with various air forces into the 21st century, with the U.S. military retiring it in the 1990s, though some nations continued to use upgraded versions.

F-4B/N/J/S: Variants used by the U.S. Navy and Marine Corps.
F-4C/D/E: Variants used by the U.S. Air Force, with the F-4E featuring an internal cannon.
RF-4B/C/E: Reconnaissance variants with specialized equipment for photographic reconnaissance.
The F-4 Phantom II's robust design and powerful engines made it a formidable aircraft, earning it a lasting place in aviation history. Its significant contributions to military aviation during the Cold War and beyond make it a classic example of American aerospace engineering.
Work in Progress, release planned 2025
Development
(To Come)Design
(To come)⚙ F4 specifications | |
| Gross Weight | 30,328 lb (13,757 kg) empty, 41,500 lb (18,824 kg) |
| Max Takeoff weight | 61,795 lb (28,030 kg) |
| Lenght | 63 ft (19.2 m) |
| Wingspan | 38 ft 5 in (11.7 m) |
| Width, wings folded | 27 ft 7 in (8.4 m) |
| Height | 16 ft 5 in (5 m) |
| Wing Area | 530 sq ft (49.2 m2) |
| Engine | 2× General Electric J79-GE-17A ABTE 11,905 lbf (52.96 kN)/17,845 lbf (79.38 kN) |
| Top Speed, sea level | Mach 2.23 |
| Cruise Speed | 510 kn (580 mph, 940 km/h) |
| Range | 370 nmi (420 mi, 680 km), ferry 1,457 nmi (1,677 mi, 2,699 km) |
| Climb Rate | 41,300 ft/min (210 m/s) |
| Ceiling | 60,000 ft (18,000 m) |
| Armament | 2x 20mm guns, see notes |
| Crew | 2 |
Combat Records
Gallery:




![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()


Photos
Videos:
The Models Corner:
-To come- Lohner E (1913)
- Macchi M3 (1916)
- Macchi M5 (1918)
- Ansaldo ISVA (1918)
- Short S.38 (1912)
- Sopwith Baby (1916)
- Short 184 (1916)
- Fairey Campania (1917)
- Sopwith Cuckoo (1917)
- Felixstowe F.2 (1917)
- Friedrichshafen FF 33 (1916)
- Albatros W4 (1916)
- Albatros W8 (1918)
- Hanriot HD.2
- Grigorovich M5 (1915)
- Grigorovich M9 (1916)
- IJN Farman MF.7
- IJN Yokosho Type Mo
- Yokosho Rogou Kougata (1917)
- Yokosuka Igo-Ko (1920)
- Curtiss N9 (1916)
- Aeromarine 39
- Vought VE-7
- Douglas DT (1921)
- Boeing FB.5 (1923)
- Boeing F4B (1928)
- Vought O2U/O3U Corsair (1928)
- Blackburn Blackburn (1922)
- Supermarine Seagull (1922)
- Blackburn Ripon (1926)
- Fairey IIIF (1927)
- Fairey Seal (1930)
- LGL-32 C.1 (1927)
- Fokker T.II (1921)
- Caspar U1 (1921)
- Dornier Do J Wal (1922)
- Rohrbach R-III (1924)
- Mitsubishi 1MF (1923)
- Mitsubishi B1M (1923)
- Yokosuka E1Y (1923)
- Nakajima A1N (1927)
- Nakajima E2N (1927)
- Mitsubishi B2M (1927)
- Nakajima A4N (1929)
- CANT 18
WW1
✠ K.u.K. Seefliegerkorps:
 Italian Naval Aviation
Italian Naval Aviation
 RNAS
RNAS
 Marineflieger
Marineflieger
 French Naval Aviation
French Naval Aviation
 Russian Naval Aviation
Russian Naval Aviation
 IJN Air Service
IJN Air Service
 USA
USA
Interwar
 Interwar US
Interwar US
 Interwar Britain
Interwar Britain
 Interwar France
Interwar France
 Interwar Netherlands
Interwar Netherlands
 Interwar Germany
Interwar Germany
 Interwar Japan
Interwar Japan
 Interwar Italy
Interwar Italy
- Curtiss SOC seagull (1934)
- Grumman FF (1931)
- Curtiss F11C Goshawk (1932)
- Grumman F2F (1933)
- Grumman F3F (1935)
- Northrop BT-1 (1935)
- Grumman J2F Duck (1936)
- Consolidated PBY Catalina (1935)
- Brewster/NAF SBN-1 (1936)
- Curtiss SBC Helldiver (1936)
- Vought SB2U Vindicator (1936)
- Brewster F2A Buffalo (1937)
- Douglas TBD Devastator (1937)
- Vought Kingfisher (1938)
- Curtiss SO3C Seamew (1939)
- Douglas SBD Dauntless (1939)
- Grumman F4F Wildcat (1940)
- F4U Corsair (NE) (1940)
- Brewster SB2A Buccaneer (1941)
- Grumman TBF/TBM Avenger (1941)
- Consolidated TBY Sea Wolf (1941)
- Grumman F6F Hellcat (1942)
- Curtiss SB2C Helldiver (1942)
- Curtiss SC Seahawk (1944)
- Grumman F8F Bearcat (1944)
- Ryan FR-1 Fireball (1944)
- Douglas AD-1 Skyraider (1945)
Fleet Air Arm
- Fairey Swordfish (1934)
- Blackburn Shark (1934)
- Supermarine Walrus (1936)
- Fairey Seafox (1936)
- Blackburn Skua (1937)
- Short Sunderland (1937)
- Blackburn Roc (1938)
- Fairey Albacore (1940)
- Fairey Fulmar (1940)
- Grumman Martlet (1941)
- Hawker sea Hurricane (1941)
- Brewster Bermuda (1942)
- Fairey Barracuda (1943)
- Fairey Firefly (1943)
- Grumman Tarpon (1943)
- Grumman Gannet (1943)
- Supermarine seafire (1943)
- Blackburn Firebrand (1944)
- Hawker Sea Fury (1944)
IJN aviation
- Yokosuka E6Y (1930)
- Aichi D1A "Susie" (1934)
- Mitsubishi A5M "Claude" (1935)
- Nakajima A4N (1935)
- Yokosuka B4Y "Jean" (1935)
- Mitsubishi G3M "Nell" (1935)
- Nakajima E8N "Dave" (1935)
- Kawanishi E7K "Alf" (1935)
- Nakajima B5N "Kate" (1937)
- Kawanishi H6K "Mavis" (1938)
- Aichi D3A "Val" (1940)
- Mitsubishi A6M "zeke" (1940)
- Nakajima E14Y "Glen" (1941)
- Nakajima B6N "Jill" (1941)
- Mitsubishi F1M "pete" (1941)
- Aichi E13A Reisu "Jake" (1941)
- Kawanishi E15K Shiun "Norm" (1941)
- Nakajima C6N Saiun "Myrt" (1942)
- Yokosuka D4Y "Judy" (1942)
- Kyushu Q1W Tokai "Lorna" (1944)
Luftwaffe
- Arado 196 (1937)
- Me109 T (1938)
- Blohm & Voss 138 Seedrache (1940)
Italian Aviation
- Savoia-Marchetti S.55
- IMAM Ro.43/44
- CANT Z.501 Gabbiano
- CANT Z.506 Airone
- CANT Z.508
- CANT Z.511
- CANT Z.515
French Aeronavale
- GL.300 (1926-39)
- Levasseur PL.5 (1927)
- Potez 452 (1935)
- Loire 210 (1936)
- Loire 130 (1937)
- LN 401 (1938)
Soviet Naval Aviation
- Shavrov SH-2 (1928)
- Tupolev TB-1P (1931)
- Beriev MBR-2 (1930)
- Tupolev MR-6 (1933)
- Tupolev MTB-1 (1934)
- Beriev Be-2 (1936)
- Polikarpov I16 naval (1936)
- Tupolev MTB-2 (1937)
- Ilyushine DB-3T/TP (1937)
- Beriev Be-4 (1940)
-
Skoda Š-328V
R-XIII Idro
Fokker C.XI W (1934)
Rogožarski PVT-H (1938)
WW2
- De Havilland Sea Vixen
- Hawker Sea Hawk
- Supermarine Scimitar
- Blackburn Buccaneer
- Hawker Sea Harrier
- Douglas A4 Skyhawk
- Grumman F9F Panther
- Vought F8 Crusader
- McDonnell-Douglas F-4 Phantom-II
- North Am. A5 Vigilante
- TU-142
- Yak 38 forger
☢ Cold War
✧ NATO
 Fleet Air Arm
Fleet Air Arm
 US Navy
US Navy
☭ Warsaw Pact
Merch
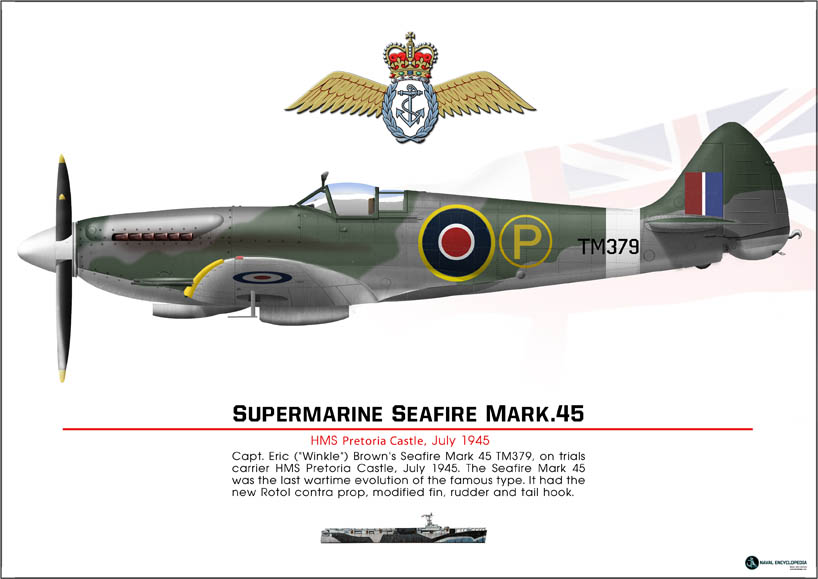
Seafire Mark 45; HMS Pretoria Castle
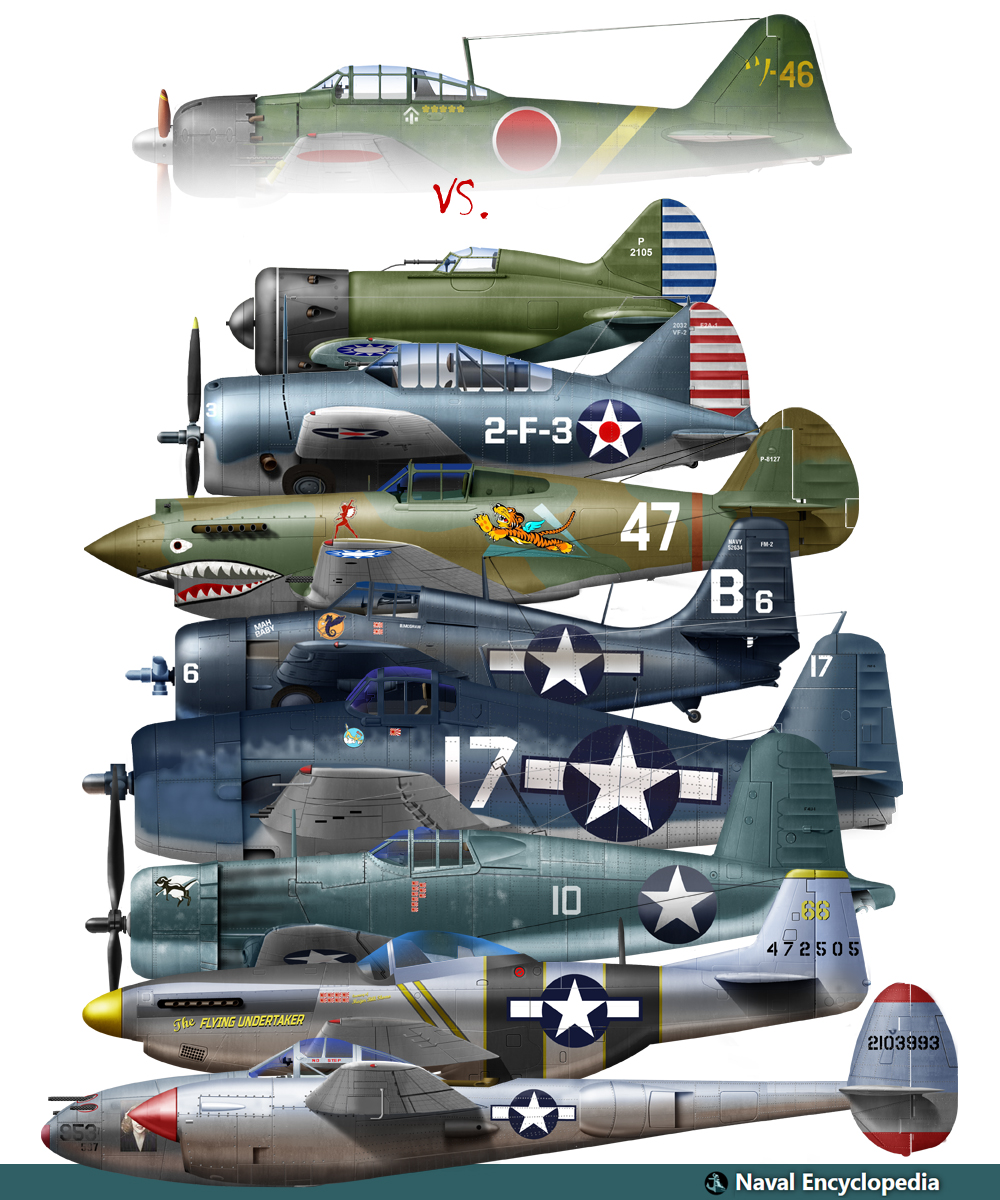

Zeros vs its aversaries

Aichi D3A “Val” Junyo
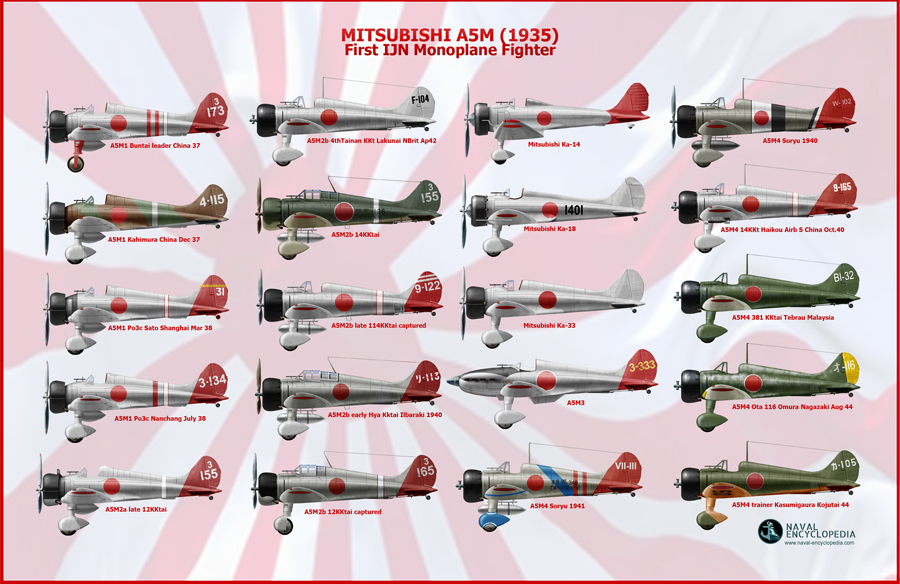

Mitsubishi A5M poster

F4F wildcat
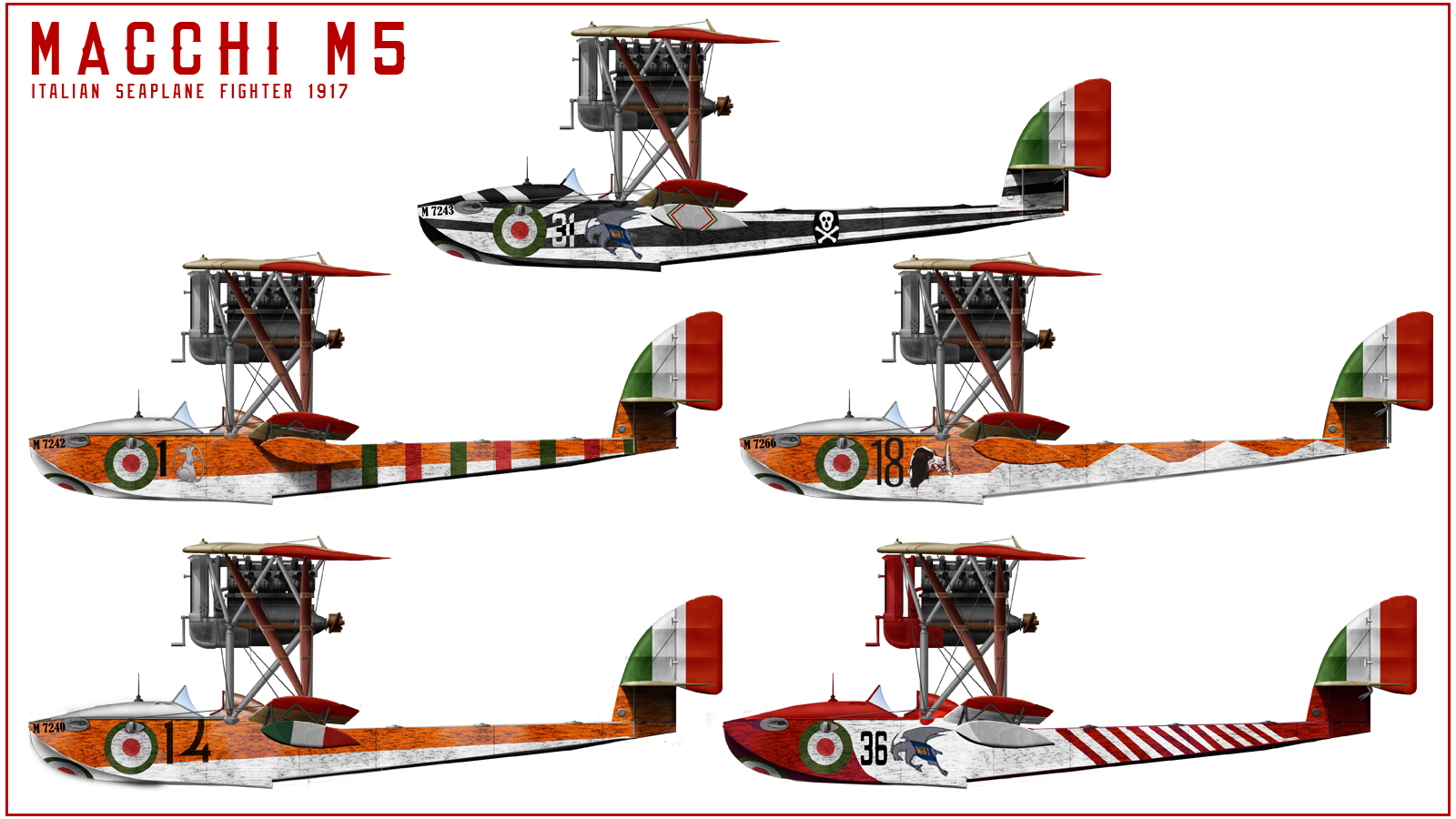

Macchi M5
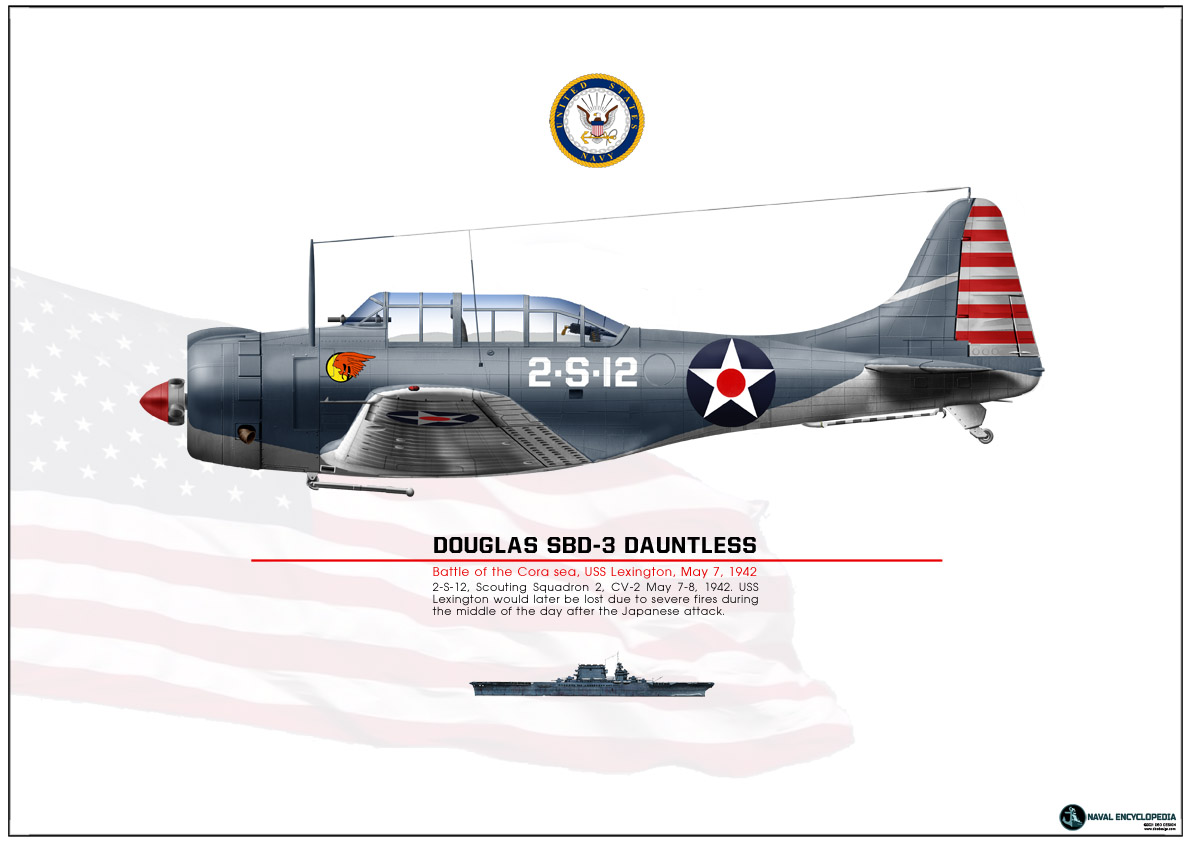
SBD Dauntless Coral Sea
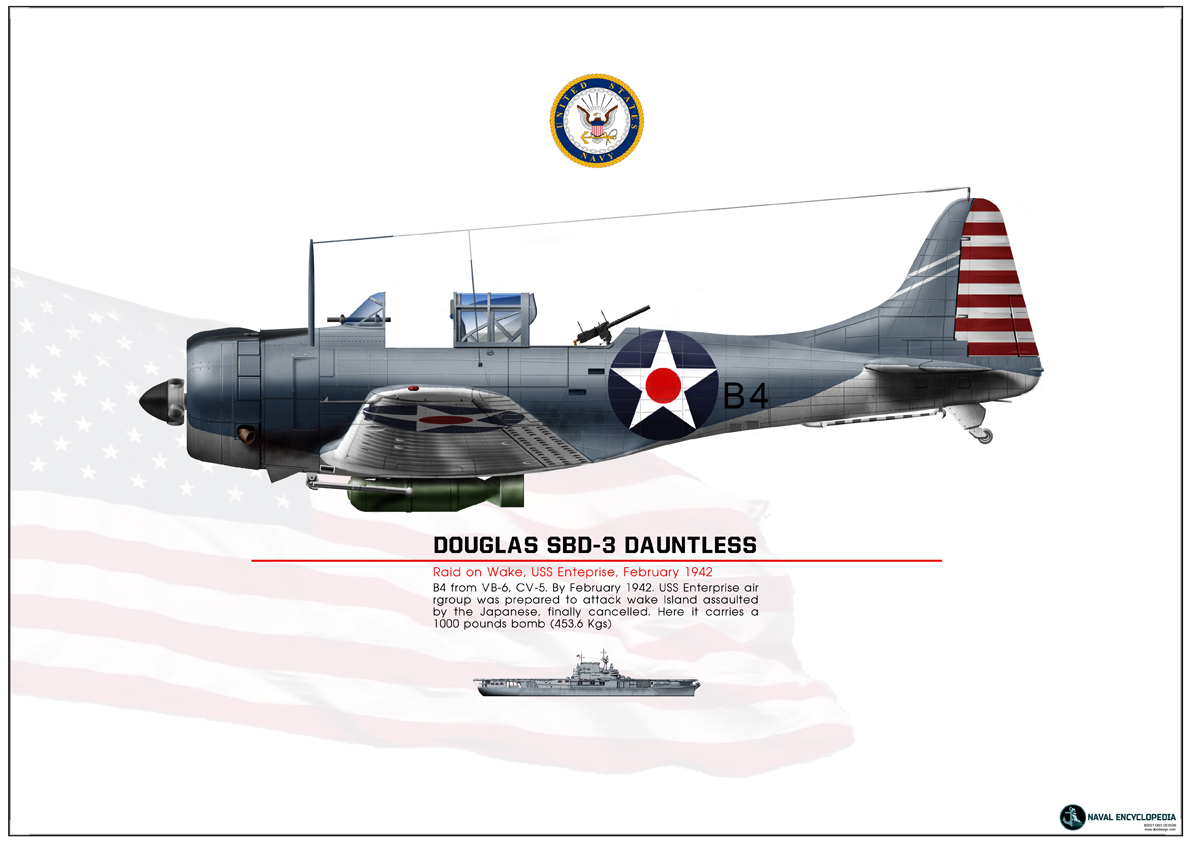
SBD Dauntless USS Enterprise

SBD-4 CV22
